
Interprofessional Education (IPE):
Interprofessional Education (IPE) is an approach to teaching and learning that brings together students from two or more professions to learn about, from, and with each other to enable effective collaboration and improve health outcomes.
The key benefits of IPE include:
- Fostering mutual understanding and respect for the roles, responsibilities, and expertise of different healthcare professionals
- Enhancing communication and collaboration skills for effective teamwork
- Promoting a patient-centered approach to healthcare delivery
- Preparing students for the realities of modern, complex healthcare systems
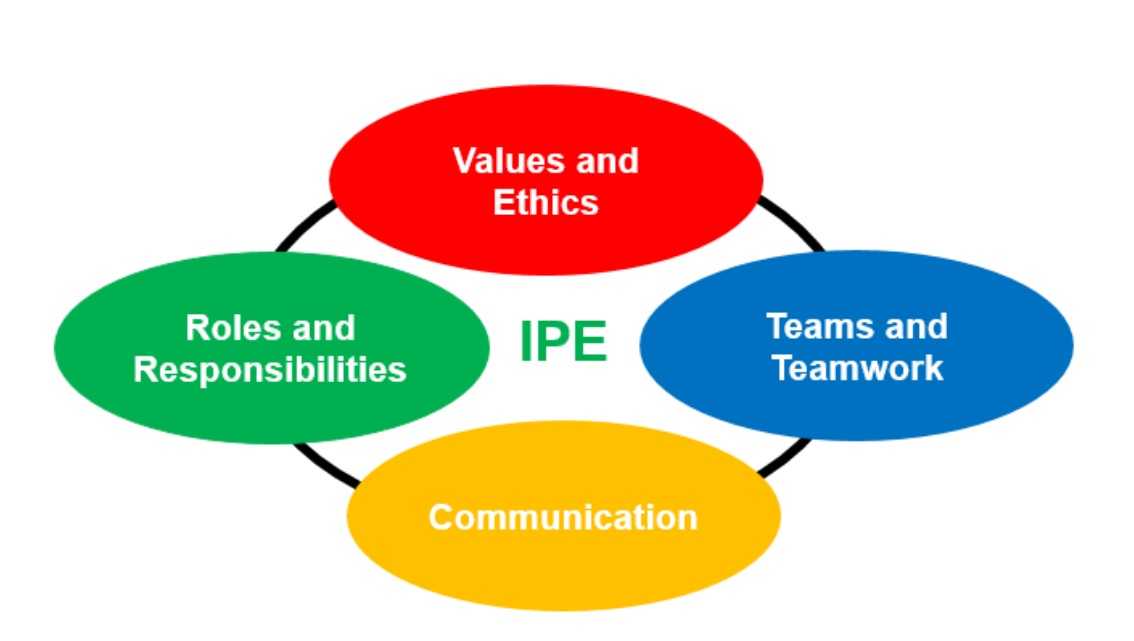
The core competencies for IPE:
- Values/Ethics for Interprofessional Practice: Work with individuals of other professions to maintain a climate of mutual respect and shared values. Demonstrate mutual respect, trust, integrity, high standards of ethics while valuing differences when working with members of other health professions.
- Roles/Responsibilities: Use the knowledge of one’s own role and those of other professions to appropriately assess and address the health care needs of the patients and populations served. Understand the roles and responsibilities of different health care professionals on the team in providing safe, efficient, and effective patient-centered health care that optimizes outcomes.
- Interprofessional Communication: Communicate with patients, families, communities, and other health professionals in a responsive and responsible manner that supports a team approach to the maintenance of health and the treatment of disease. Communicate effectively by responding respectfully, listening actively, and seeking common understanding.
- Teams and Teamwork: Apply relationship-building values and principles of team dynamics to perform effectively in different team roles to plan and deliver patient-/population-centered care that is safe, timely, efficient, effective, and equitable. Demonstrate effective teamwork by applying principles of team dynamics, process improvement, and conflict management.
IPE can be achieved by adopting three Phases:
Phase 1: The exposure phases
In this phase, the organization serves largely as a precursor and is designed to bring learners together with peers who represent other health professions.
Phase 2: The immersion Phase
Calls for cooperative interactions that support students’ concentration on learning from, about, and with each other’s professions.
Phase 3: Mastery Phase
The integration of critical thinking and problem-solving in challenging real-world scenarios is necessary for the mastery phase.
Team-based care that concentrates on complicated care areas is an example of mastery activities.



